
- #WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN .EXE#
- #WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN INSTALL#
- #WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN UPDATE#
- #WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN CODE#
"sudo apt install libpulse0:i386/testing"), and then continue to install Wine. To solve this install the i386 package from the same suite as the already installed amd64 package (e.g. Debian Backports or Unstable) then some newly needed i386 packages might have another version, and you face broken dependencies. But if you install Wine from another suite (e.g.

These packages are the versions from your default release, e.g. Usually you already have most of the required amd64 library packages installed. amd64 and i386 to be in exactly the same version. It's quite easy to run into broken dependencies when installing Wine: The multiarch setup requires packages from e.g. To run 32-bit Windows applications (this is the most common case, independently of your Debian architecture) make sure that wine32 (or wine32-development) is installed (requires step 1).

This should automatically install all other required packages if you already have enabled multiarch (step 1). You always need to install the wine (or wine-development) package.
#WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN UPDATE#
Enable it with the following command: sudo dpkg -add-architecture i386 & sudo apt update for amd64 (which most users have) you need i386. You can identify your architecture with the following command: dpkg -print-architectureĮ.g. This is needed for running 32-bit Windows applications (many modern apps are still 32-bit), but also for large parts of the Windows subsystem itself. On 64-bit systems you should enable a 32-bit architecture for multiarch. If you install both sets, "wine" will take precedence unless you configure your system otherwise, see "Usage" below. You can either install both sets at the same time, or only one of them. Do not mix this up with the *-dev packages which contain the header files and development libraries. version 5.12).ĭespite its name wine-development is also intended to be used by regular users.
version 5.0.1), and wine-development the development releases (e.g. Wine tracks the stable releases from (e.g. Since Debian Jessie you can choose between two sets of Wine packages: wine and wine-development.
#WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN .EXE#
exe file like PuTTY on your system and open it with Wine as below screenshot or use following command. To use wine we need to login to the Debian desktop system. Use the following command to check the version of wine installed on your system wine -version Wine installation successfully completed. So set the wine bin directory to the PATH environment to access commands system-wide. The wine packages are installed under /opt/wine-stable directory. Sudo apt install -install-recommends winehq-stable The –install-recommends option will install all the recommended packages by winehq-stable on your system. Update the apt information with the newly added repositories. Use one of the following commands to enable the Wine apt repository in your system based on your operating system and version. Also, import the GPG key to your system by which the wine packages are signed. In order to run Winehq, You need to enable i386 architecture on your Debian system. This article will help you to install Wine 5.0 Stable Release on Debian 10 Buster Linux system using the official repository. Wine is an Open Source implementation of the Windows API and will always be free software. You may also use the package manager to install wine.
#WINE EMULATOR DEBIAN CODE#
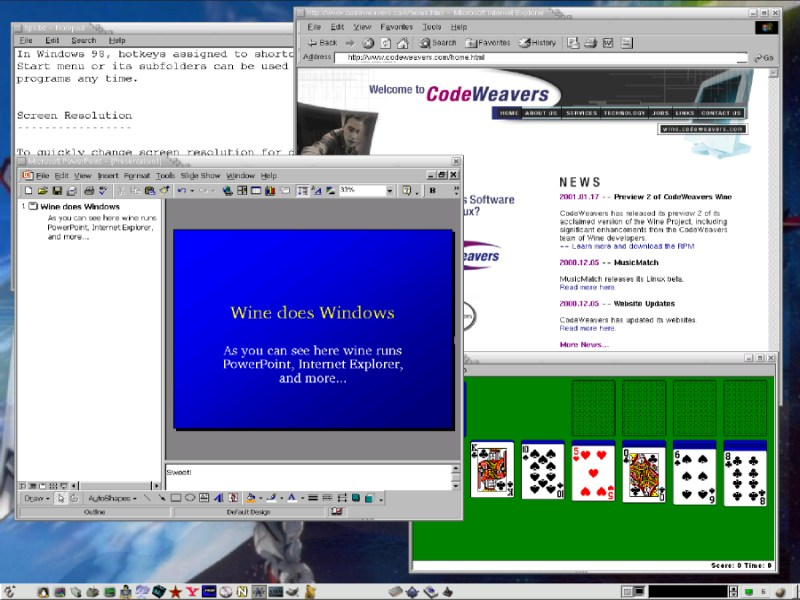
Its source code is available for download from its official site. The Winehq team has announced the latest stable release 5.0 on Jan 21, 2020. Wine (originally an acronym for “Wine Is Not an Emulator”) is a compatibility layer capable of running Windows applications on several POSIX-compliant operating systems, such as Linux, macOS, & BSD.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
